Three key databases for teams, and how to use them
Databases allow you to create and categorize your company’s information - from all hands meeting notes, to project briefs, tasks to do, and more. With databases for your meeting notes, docs, tasks, and projects, you can keep everything organized and easy to find in an instant.
- Easily surface information in three essential databases
- 1. Meeting Notes
- 2. Docs
- 3. Tasks & Projects
- Customize databases to see what you need, when you need it
- Every item in a database is a fully editable page
- Use properties to add dimensions of information to pages
- View information in different ways
- Create contextual views
- Use groups and sorts to arrange information
- Save views to display filtered sets of information
- Bring together data from different sources into one block
- Resources
Databases are powerful, digital filing cabinets where you can organize pages and add layers of information to each item. Instead of your documents getting lost in hidden folders, databases give everyone visibility into what’s happening across the company. You have the flexibility to view your information in different ways and create context-specific filters and views.
And, if you need a doc or a task to show up somewhere else, there’s no need to copy and paste plain text. You can resurface information dynamically across the workspace, wherever it’s relevant.
Want to view all your team’s tasks for the week grouped by the assignee, standardize and speed up documentation, or design a project dashboard uniting all relevant meetings, documents, and tasks?
You can do all this and more with three databases that are essential for every team: Meeting Notes, Docs, and Tasks & Projects
We’ve created templates for all three of these databases, which are linked below. You can copy them straight into your workspace and they’ll be ready to use with your team. This will be rolling out to all users in the coming weeks. If you don’t yet see it in your workspace, you will soon!

Go straight to the templates
Check out our in-app template picker here.
If you’re using Notion for knowledge management, you might be keeping everything from last week’s all-hands meeting notes to the product team’s latest project scope and quarterly OKRs somewhere in your workspace.
We show you how to create an easy-to-navigate company wiki, with top-level pages and sub-pages living within them here. But, you’ll also need databases if you want to avoid a cluttered workspace, where team members have to dive into pages within pages to find what they’re looking for.
Let’s take a closer look at how you could use Meeting Notes, Docs, and Tasks & Projects databases in your company workspace.
1. Meeting Notes
If everyone who attends a meeting jots down their own disconnected notes, there’s no guarantee you’ll leave with clear takeaways. Plus, it’s not easy to refer back to what was said.
A meeting notes database will help your team become more methodical about note-taking. Meetings stay on track, and everyone knows the next steps.
Here are some things you can do with your meeting notes database:
Use properties to categorize meetings — Add a meeting date, and use a
Personproperty to tag all attendees. With aSelectproperty, add meeting type tags to indicate whether it’s a standup, weekly sync, etc.Choose a list layout sorted by date — Select
Sort, byDate, andDescendingto view the most recent meetings first.Group or filter according to meeting type — If you want to review notes from the design team’s recent meetings, you can group the database by meeting type or attendees. You can then save those filtered views to come back to in future.
Take meeting notes inside the database entry — When a new meeting takes place, simply create a new item in the database, fill in relevant properties and start taking notes.
Use templates to speed up note-taking and improve accuracy — Set up a template for each different kind of recurring meeting. Inside the template, have key properties already filled out where possible. Add some page content like bullet points, a checklist and some useful headings so you can jump straight into note-taking as the meeting begins.
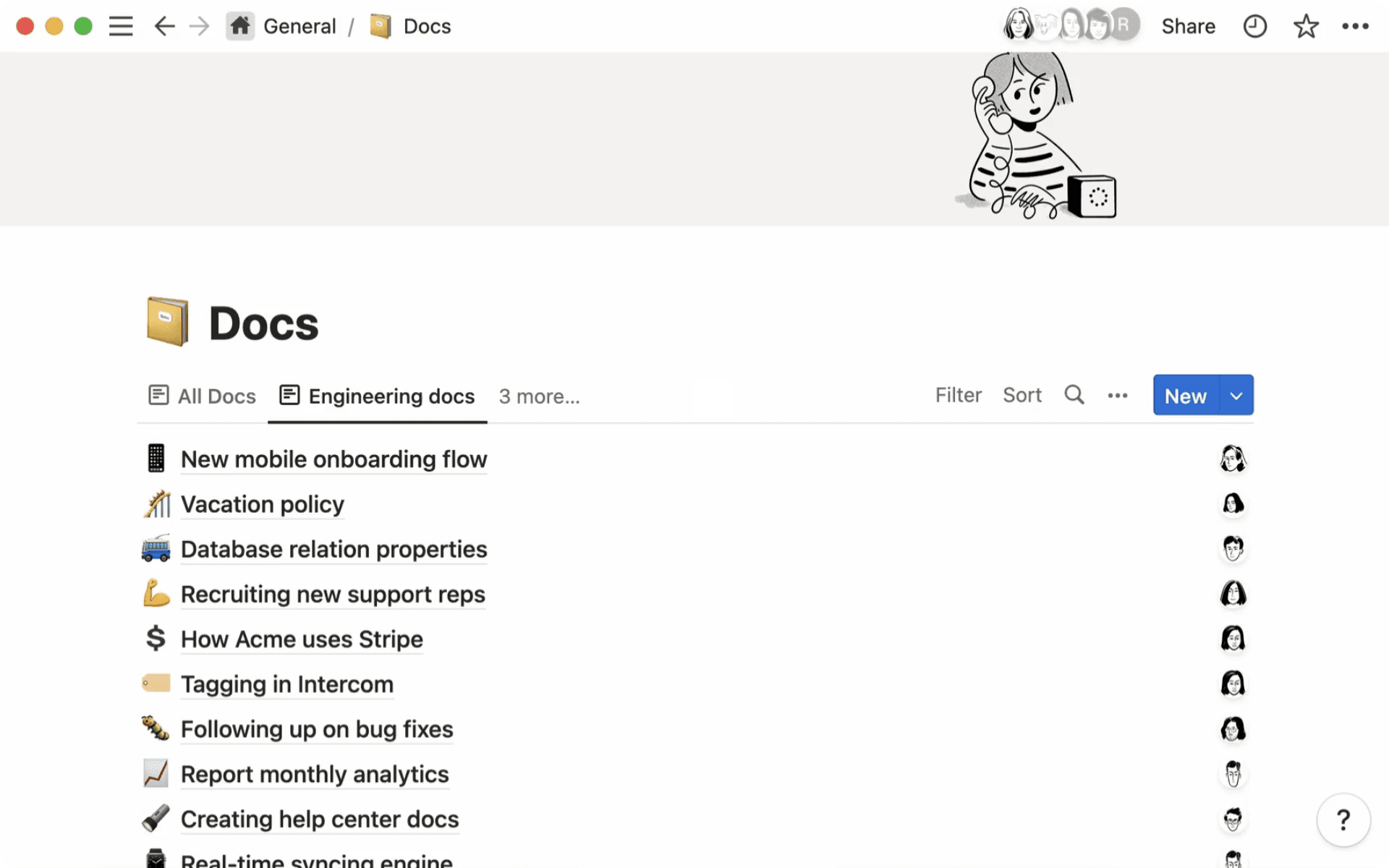
2. Docs
Clear documentation results in greater transparency and gives everyone accountability for their work. Your docs database can become the single source of truth for company information. You can have one docs database for the whole company, and then create synced views within each department’s teamspace.
Here are some tips for using your docs database:
Add dimensions of information to each document — Documents in your docs database are much more than just pages stored in folders. With properties, you can add more context compared to a regular document, from dynamic properties like created date and last edited date, to select properties to label documents and status property to tag docs as In Progress, Complete, etc.
Create templates for often-used documents — Fill out properties and add an outline of page content so you never have to draw up a technical spec, architecture overview, or project scope from scratch.
Format documents aesthetically — Inside the page, you can organize text into columns, headers, bullets, checklists, images, embeds, and more. It’s up to you to design your documents however makes the most sense. You can even embed databases within the page, or sync content from other tools like GitHub and Jira.
3. Tasks & Projects
Task and project management is a breeze if you use a database to track all your team’s to-dos.
Tasks & Projects are two related databases that work together to help you connect the dots between daily jobs to do and larger objectives.
Here’s how you can manage your tasks and projects in Notion:
Add new tasks as separate entries into the database — Make sure to enter all tasks into your database to ensure nothing ever slips through the cracks.
Tag each task with properties — Status property, assigned, and due dates can help you see what tasks need to be done, and by who.
Select a project for each task — Projects are made up of a series of tasks. Create a separate database for tasks, and use a relation property to connect them. That way, you can attach tasks to relevant projects, and you can see how close your projects are to completion.
Group tasks by project, assignee, or due date — Easily see all tasks by their corresponding project or due date. Grouping tasks by assignee is a great way to see what each of your team members has on their plate.
Use a progress bar to show project completion — You can add a satisfying progress bar to show how close you are to completing your projects. First, add a rollup property to your projects database. When you edit the relation, choose “Tasks”, and select the status property. Then, select “Calculate percent per group” and choose “complete.” Now, whenever you move tasks into “completed” you’ll see your progress bar move closer to 100%.
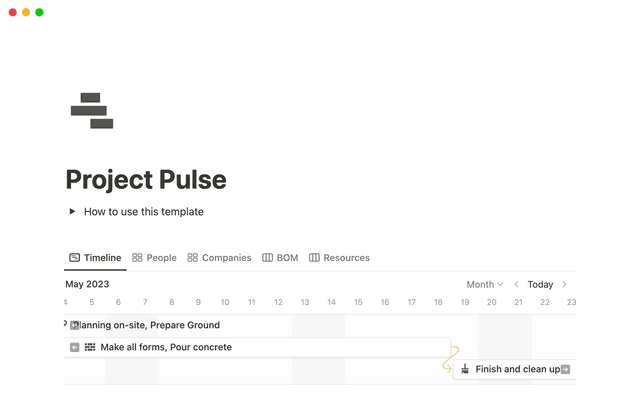
View ongoing projects on a timeline — See how different project commitments cross over by creating a timeline view of projects. Make sure your projects have a start and end date so you can visualize their duration.
Creating a database is easier that you might think. While you can start from scratch, we've simplified the process with pre-selected properties to get you going quickly. To get started—-
Open a new page and click
Databaseat the bottom of the page.From there, you have the option to start from scratch or build with AI.
Let's say you want to build a simple project tracker to monitor your team's key initiatives this quarter. Select "Projects" from the suggested databases. You'll then be presented with options to select or deselect the most relevant properties for your database. Pick and choose the ones that make sense for your team - you can always adjust them later. Just like that, you've got your project tracker ready to go!
Whether you have something specific in mind or want inspiration, you have plenty of options - from popular templates to AI-guided setup. Now that you’re all set up, let’s dive into some database to help you get your database up and running in your workspace.
Every item in a database is a fully editable page
To add a new page to a database click + New at the bottom or the New button at the top right. This creates a new, fully customizable page that lives inside the database. You can tag this page with intelligent properties according to the structure of the database.
You can also create page templates inside the database to help you speed up and standardize your work.
To create a template, just click New template. Anything you add to this page will be saved as a template that you can recreate automatically in the future. Include any information that you want to appear every time, whether it’s properties you want to fill out or page content like headers, bullet lists, or prompts. You can create various templates for each database so you don’t always have to create pages from scratch.
Use properties to add dimensions of information to pages
Properties allow you to categorize database entries in just about any way you can imagine. Basic properties allow you to add text, numbers, custom tags, person tags, dates, and more. With advanced properties you can relate one database to another, pull through specific information from another database, and even build custom formulas.
Full a full list of database properties and learn more about them here.

Choose from customizable pre-built properties
View information in different ways
To customize a database layout, go to the options menu (…) and select Layout. Here you can choose between table, list, board, calendar, or timeline layouts.
Tables give you an overview of all your documents — Tables are the default database layout and they’re great for large sets of information, or when you want to see everything in a database.
Lists are a simplified way to view items — For an uncluttered view of your recent meeting notes, you could use a list database.
Board view can help keep track of your team’s tasks — Kanban board databases are ideal for project or task management. You can group the board database by the status property, so you easily move cards across from In Progress to Done for example.
View launch or publish deadlines on a calendar — Calendar layouts are useful when you want to see database entries plotted by date. You can use a calendar to see when content goes live or when new features are due for release.
Timelines let you visualize your workload and deadlines — If you’re managing a team, timelines can be a helpful way to look at projects because you can see how much you have on your plate at any one time.
You don’t have to decide on just one layout per database. One database can contain multiple views. To add a new view, click + next to the current view, and you can add a different layout. you can then switch between different database views using the tabs at the top of your database.

Learn more about database views
To learn more about database views and how they can be used, check out this video guide.
Create contextual views
As your database grows, you need a way to view information that’s relevant to different situations. By using filters, you can display subsets of information based on properties. So, if you want to view documents related to a certain project, or notes from all of last week’s meetings, you can use filters to show these entries, and hide everything that’s not relevant.
To quickly filter your database, click Filter and choose the property you want to filter by. Here are some examples of ways you might filter databases:
View all meetings that took place in the last week — Use a date filter to view all meetings that took place during the last week, tasks due this week, or content to be published in the next month.
See all tasks in progress — Filter by status to only show tasks that are currently tagged “In Progress”.
Filter to see one type of document — Use a filter to show only certain types of documents.
View tasks assigned to you — Filter by person to see all tasks assigned to you, or meetings you attended.
Focus on high-priority tasks — Display only projects or tasks that you’ve marked as priority.
If you want to apply more than one filter, you can also select Add advanced filter. From here you can add as many filters as you need.
So, you could filter your tasks database to show all tasks that due this week, assigned to you, and ready to start.
Use groups and sorts to arrange information
You can group together items based on properties, so you could separate items in the database by status, assignee, due date, document type, and more.
In a board view, grouping changes how the cards are arranged on the board. When you group a table, you’ll see that the database splits into sub-tables according to groups.
Another way to organize information in a database is through sorting. You can sort entries in a database to put them in order of date created, due date, or sort alphabetically according to titles or tags.
Save views to display filtered sets of information
Now, to combine the power of filters and views, you can create multiple views in a single database, each filtered to show a different set of information.
Then, you can tab across your database to view different information depending on what you need to see. For example, within one database you can have:
An overall view of everything in the database — This could be a table database filtered to show all tasks not marked “Done”.
A kanban board grouped by status — You can easily drag tasks across from “In Progress” to “Done” in a board view layout.
A weekly view of everything due this week — A list view filtered by date can show everything you need to get done this week.
A personal view of items assigned to you — Focus on your own to-do list by filtering to show only items assigned to you.
Bring together data from different sources into one block
To create another view of a database anywhere in the workspace, hit “/” and choose “Linked view of database”. Instead of creating a view from scratch, you can choose an existing data source to import.
Linked database views allow you to bring relevant information across into different areas of the workspace without duplicating your work. You can create contextual views of a database with custom filters and views applied.
You can even bring source data from various databases to display as different views in the same database block. This allows you to create dashboards to view relevant information side by side.
To create a project dashboard, you could create one database block which unites all the tasks, documents, and meeting notes related to that project, which would appear as different views in the same database.

To access the Notion template gallery, click on Templates in the sidebar
Something we didn’t cover?